Introduction: Have you ever wondered why you feel more alert and energetic during the day and sleepy at night? Or why you find it challenging to adjust to a new time zone when traveling? The answer lies in your body’s internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm. This biological phenomenon plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including sleep-wake cycles, hormone production, body temperature, and even cognitive function. In this blog post, we’ll explore the fascinating world of the circadian rhythm in healthy individuals and its significance in maintaining overall well-being.
What is the Circadian Rhythm? The term “circadian” comes from the Latin words “circa” (meaning “around”) and “diem” (meaning “day”). Essentially, the circadian rhythm refers to a roughly 24-hour cycle that governs the timing of various physiological processes in our bodies. This internal clock is regulated by an intricate network of genes, proteins, and specialized cells located in the hypothalamus of the brain, specifically in an area called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN).
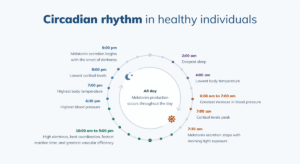
Key Components of the Circadian Rhythm:
- Sleep-Wake Cycle: One of the most well-known aspects of the circadian rhythm is the sleep-wake cycle. The circadian clock influences our sleep patterns, determining when we feel most alert and when we naturally feel sleepy. The hormone melatonin, which is released by the pineal gland in response to darkness, helps regulate this cycle.
- Hormone Production: The circadian rhythm also affects the production and release of various hormones in our body, including cortisol, growth hormone, and testosterone. These hormones follow a distinct pattern throughout the day, influencing metabolism, energy levels, and overall physiological function.
- Body Temperature: Our body temperature fluctuates in accordance with the circadian rhythm. It tends to be at its lowest during the early hours of the morning and gradually rises as we approach midday. These temperature variations have an impact on our alertness, cognitive performance, and physical endurance.
- Metabolism and Digestion: The circadian rhythm influences our metabolism and digestion, with certain metabolic processes being more active during specific times of the day. Disruptions in this rhythm, such as irregular eating patterns or night-shift work, can lead to metabolic disorders and digestive issues.
The Importance of a Healthy Circadian Rhythm: Maintaining a well-functioning circadian rhythm is vital for overall health and well-being. Here are a few reasons why:
- Quality Sleep: A balanced circadian rhythm promotes healthy sleep patterns, allowing you to fall asleep more easily, experience restorative sleep, and wake up feeling refreshed and energized.
- Cognitive Performance: The circadian rhythm plays a significant role in cognitive function, including memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities. A disrupted rhythm can impair cognitive performance and increase the risk of cognitive disorders.
- Mood and Mental Health: Studies have shown a strong link between circadian rhythm disruptions and mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder. A stable rhythm helps regulate mood and emotional well-being.
- Physical Health: The circadian rhythm influences numerous physiological processes, including immune function, cardiovascular health, and metabolism. Disruptions to the rhythm have been associated with an increased risk of chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Circadian Rhythm: To support a well-functioning circadian rhythm, consider the following tips:
- Establish a Regular Sleep Schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Consistency helps regulate your internal clock.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it cool, dark, and quiet. Limit exposure to electronic devices before bedtime as the blue light can disrupt melatonin production.
- Prioritize Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise, especially during daylight hours, can help regulate your circadian rhythm and improve sleep quality.
- Practice Healthy Eating Habits: Aim for regular mealtimes and avoid heavy meals close to bedtime. Limit caffeine and alcohol intake, as they can interfere with sleep.
- Expose Yourself to Natural Light: Natural light exposure during the day helps regulate the circadian rhythm. Spend time outdoors, particularly in the morning, to help synchronize your internal clock.
Conclusion: The circadian rhythm is a fascinating phenomenon that governs our internal clock and influences various aspects of our health and well-being. By understanding and respecting our body’s natural rhythm, we can optimize our sleep patterns, enhance cognitive function, and promote overall physical and mental health. Prioritizing a healthy circadian rhythm is a powerful step towards leading a balanced and fulfilling life.



