Introduction
Testosterone, often referred to as the “male hormone,” plays a crucial role in various physiological functions in both men and women. From influencing muscle mass and bone density to regulating mood and energy levels, testosterone is a key player in maintaining overall health. In recent years, researchers have explored the intricate relationship between glutathione and testosterone production, shedding light on how this powerful antioxidant contributes to hormonal balance in the human body.
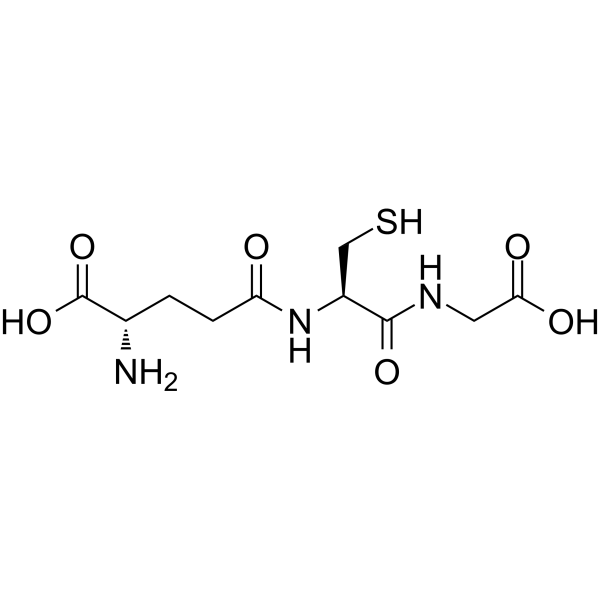
Understanding Glutathione
Before delving into the connection between glutathione and testosterone, it’s essential to grasp the role of glutathione in the body. Glutathione is a tripeptide composed of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine. Found in every cell, glutathione is a master antioxidant that safeguards cells from oxidative stress and supports various cellular functions.
Oxidative Stress and Testosterone
Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, can negatively impact testosterone production. Free radicals, highly reactive molecules, can damage cells, including Leydig cells in the testes responsible for testosterone synthesis. Glutathione steps in as a potent antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and protecting Leydig cells from oxidative damage.
The Glutathione-Testosterone Connection
- Detoxification of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Glutathione actively participates in detoxifying reactive oxygen species, a type of free radical produced during normal metabolic processes. By scavenging ROS, glutathione helps maintain the integrity and functionality of Leydig cells, promoting optimal testosterone production.
- Supporting Enzymatic Reactions: Glutathione is involved in several enzymatic reactions essential for testosterone synthesis. One such enzyme is 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, which catalyzes a key step in the conversion of cholesterol to testosterone. Glutathione’s presence is crucial for the proper functioning of this enzyme, ensuring a smooth testosterone production process.
- Reducing Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can negatively impact testosterone levels. Glutathione’s anti-inflammatory properties help mitigate inflammation, creating a favorable environment for Leydig cells to produce testosterone without interference from inflammatory mediators.
- Recycling Antioxidants: Glutathione doesn’t just act as a direct antioxidant; it also plays a vital role in recycling other antioxidants like vitamins C and E. This recycling process ensures a continuous supply of antioxidants in the body, further protecting Leydig cells from oxidative stress and promoting optimal testosterone production.
Practical Approaches to Boosting Glutathione Levels
Given the critical role of glutathione in supporting testosterone production, maintaining optimal levels of this antioxidant becomes paramount. Here are some practical approaches to enhance glutathione levels:
- Dietary Sources: Include sulfur-rich foods in your diet, such as garlic, onions, cruciferous vegetables, and eggs. These foods provide the necessary building blocks for glutathione synthesis.
- Supplementation: Consider supplementing with precursors to glutathione, such as N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and alpha-lipoic acid. These supplements can enhance glutathione levels indirectly.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, as exercise has been shown to boost glutathione levels. Aim for a combination of aerobic and resistance training for optimal results.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep, as it is during sleep that the body undergoes various repair and regeneration processes, including the synthesis of glutathione.
Conclusion
In conclusion, glutathione emerges as a crucial player in maintaining testosterone production by protecting Leydig cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. By understanding and supporting the intricate interplay between glutathione and testosterone, individuals can take proactive steps to promote hormonal balance and overall well-being. Incorporating a healthy lifestyle, dietary choices, and targeted supplementation can contribute to the optimization of glutathione levels and, consequently, support optimal testosterone synthesis in the human body.



